
The economics relating to climate change is a subject of great uncertainty. The economic effects of climate change can be difficult to quantify in monetary terms. It is difficult to know exactly how much damage will occur, how long it will take to resolve the problem, and what the benefits of mitigation or adaptation will be. This uncertainty is magnified when the issue is global.
A temperature rise of 3oC is the most common estimate of the impacts of increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide emission by doubling it. This would translate into a global cost of 0.5% GDP per year by the mid-century. This figure could be lower. It is possible that the cost of a fully functioning economy would be even lower.
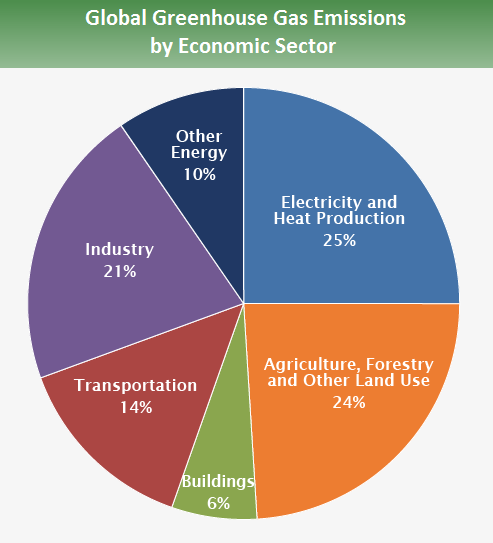
Integrated assessment models (IAMs), a type that allows you to include costs from different scenarios, are called integrated assessment models. These models can be used for assessing the impact of a policy. IAMs consider a wide range of factors including technological advancements, economic growth, demographics and environmental changes. The effects on climate policies can be analyzed in monetary terms with an integrated model.
You can capture the social costs of carbon by using a discount rate, among others. This method weighs the benefits of future actions against the risks of inaction. Depending upon the situation, a discount rates may not give enough weight for future events. Future consumption's value could depend on what time is available, how the environment is performing, and who receives it. The discount rate might not reflect catastrophic events such as a collapse of society.
As a result of this uncertainty, many economists have debated the merits of discounting the value of future actions. They also stressed the importance of accounting to account for high-impact, low-probability outcomes. The benefits of reaching a target are often more valuable than those that are not achieved.
Although there are uncertainties surrounding the impact of climate change, the benefits of reducing greenhouse gas emissions are clear. There are many methods to reduce GHG emission, but technological innovations that make it possible to shift to a lower-carbon economy are the best. The renewable power capacity will increase by 60% over 2020 levels by 2026. Currently, energy generated from renewable sources costs less than that of fossil fuels.

Climate change is one the most pressing issues facing the globe. Many countries have set themselves targets for net carbon neutrality before 2050. This target would require significant structural changes in both the economy, and capital markets. Nevertheless, the costs of achieving this goal are less than 0.5% of GDP by mid-century.
As a matter of fact, avoiding climate change is technically feasible. There are many uncertainties and the pace at which technological innovation can be achieved is not certain. Economic growth is unpredictable.
To address these uncertainties, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported that limiting warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius by 2060 was the safest option. Despite the risks, the international community has committed towards the 1.5 degree goal. The majority of the national governments have committed to this goal.
FAQ
What does climate change politics have to do with global efforts to combat it?
Climate change is a highly politicized issue that has created a great deal of division among nations, governments, and individuals. Politics of different actors can have an impact on the implementation of climate change measures. It has become increasingly difficult to come to an agreement on how to address this urgent environmental crisis globally.
The overwhelming majority of scientists agree with the fact that human-generated global warming is real. It is urgent for action to address it. These issues are often dominated by politics, which can hinder global cooperation that is necessary to implement sustainable energy practices, protect natural habitats, research viable technological solutions, as well as other climate change interventions.
Many governments around the globe want to protect business interests and enforce policies that restrict business activities. This often clashes with regulations that experts recommend for effectively addressing climate change. Without strong commitments of all participating countries, and international action on a large scale, it becomes difficult for any state or group or states to effectively address climate-change legislation.
Differences in power dynamics among countries further complicate gaining full consensus on how best to tackle climate change. Countries with more economic power often appoint their own representatives to represent them on international bodies responsible for negotiations over the environment - this can lead to lopsided discussions of those countries' perceived interests versus the collective interest of all involved parties. At both the national and international level, there have been extensive discussions about potential side effects of radical changes like geoengineering.
A grassroots movement has also struggled against powerful opposition, including corporate ownerships as well-funded lobbyists trying to keep their industries politically favorable. This is especially true when it comes funding research into alternative energy production and enforcing mandates for renewable energy technology. Individual governments need to be clear about the potential rewards and outcomes of making valid progress on the issue. They cannot seek short-term spectacles or gains to gain public support.
Properly distributing resources allocated towards any intervention program while being mindful of political divisions between nations will be critical if any coordinated effort aimed at mitigating our current environmental crisis is going successfully to come to fruition.
What is the impact of climate change on oceans and marine life around the world?
What will climate change do to the oceans and marine life of the world?
Since its inception climate change has significantly affected the world's oceans as well as the marine life associated with them. Constant oceanic heat from the depletion in the ozone layer causes major disruptions in marine ecosystems. This leads to coral bleaching, and decreases in species.
Climate change also causes unpredictable weather conditions and stronger storms. These extreme surges can be deadly for coastal areas. Also, rising temperatures can reduce the oxygen levels in the water system, leading to "deadzones" that are areas with less marine life.
Climate change is also contributing to ocean acidification, caused by excess carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere that accumulates within the oceans. Ocean acidification causes an increase in pH which affects the vital functions of animals such as crabs, clams, and oysters that cannot adapt to changing conditions.
Higher temperatures can also cause changes in natural habitats. They may shrink or change their geographical location, making it unhabitable for species that depend on them. The increase in ocean stresses accelerates the already high rates of extinction worldwide. This can lead to a severe imbalance among predators and prey, which could ultimately lead to complete extinction.
The ripple effect of climate change affects entire ecosystems. It can directly or indirectly impact multiple species through evaporation, lower water volumes, and sharp temperature shifts. The effects of climate change continue to impact the lives of entire species on this planet.
What is climate change and how does it occur?
Climate change refers the long-term shifts that occur in global weather patterns due to an increase in greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to global temperature rises that can result in a range of climate and weather changes. This can include rising sea levels, melting glaciers, extreme storms and droughts, widespread coral reef bleaching, species extinction, and disruptions to food production.
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. These include burning fossil fuels, transporting electricity, cutting down trees, and farming livestock. These activities emit large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into our atmosphere, which causes the planet to heat up faster than natural processes such as volcanic eruptions.
Deforestation also plays a large role contributing about 15-20% of global greenhouse gas emissions. It releases the stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere when trees are chopped down or burned. Forests also act as a natural carbon sink, removing CO2 from the atmosphere; without this absorption capacity, carbon dioxide levels around the globe will continue to rise, with disastrous consequences for ecosystems.
Other than CO2, human-caused pollutants also release other dangerous gases such as methane and nitrous oxide (N2O) into the atmosphere. Methane has been used extensively in industrial processes and contributes significantly to atmospheric warming while N2O is emitted primarily from agricultural soil management activities like fertilization or tilling which release excess levels of nitrogen into soil leading to N2O production upon microbial contact.
To minimize climate change humanity must make concerted efforts across social, economic, and political institutions to reduce these emissions drastically and transition away from our dependence on fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind power, or low-carbon hydrogen fuels. A smart approach to reducing atmospheric contamination and preventing CO2 accumulation could be to replace polluting fossil-fuel technologies with ones that encourage zero-waste living. Reforestation projects, which are powerful aid in the fight against climate change by absorbing large quantities of CO2 back into nature and maintaining biodiversity, can help us take responsibility for our environmental impact.
What role can individuals and communities play in combating climate change?
Climate change is one of the biggest contemporary challenges we face today. This is a problem that affects everyone. We must all pay attention to it and take action individually to make a difference.
Individuals play a vital role in addressing climate change and reducing its impacts. Everyday behaviors can include anything from reducing waste and consuming consciously, going through changes in lifestyle such as switching to a vegetarian diet, consuming less meat, using public transportation more often, and choosing more sustainable materials in clothing and home decor. They can also be involved in political advocacy, and encourage initiatives within their communities that foster sustainability.
It is important that communities are involved in the larger climate change effort. They can help reduce carbon emissions by promoting sustainable energy sources, improving infrastructure for electric vehicles and cycling, and encouraging waste management through composting. Collaboration between different communities across cities and countries is fundamental for achieving success in this mission.
This will help individuals become aware of the issues at stake and understand how to contribute positively to tackling them. This will enable individuals to become more aware of the issues and better understand how we are connected with other societies that are similarly affected by global warming.
Employers have a significant responsibility in combating climate change. Introducing corporate practices that are focused on sustainability and choosing green alternatives whenever feasible will undoubtedly result in positive economic and sociological outcomes.
Thus, individual actions as well as community policies combined with business transformation will greatly contribute to the creation of solutions for global warming and collectively protecting humanity from longer-term harmful effects from climate change.
What does the role of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change?
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act like an invisible blanket around the Earth, trapping infrared radiation and warming the atmosphere. Without them, the planet might be much colder that it is now.
Human activity is responsible for the emission of greenhouse gases. This includes burning fossil fuels and other industries. These activities are increasing in number, which means that more heat is trapped in our atmosphere. This can lead to extreme weather events and rising temperatures.
Carbon dioxide (CO2), the most potent greenhouse gas, is released by fossil fuels like gas, oil, and coal. Major contributors to climate disruption are methane (CH4) as well as nitrous dioxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Due to human activities, the concentration of greenhouse gasses has increased dramatically since preindustrial time. This has led to global warming and an increase in temperatures all over the world, as well as in our oceans. It is also leading to changes such as intense storms and droughts; melting glaciers; and rising seas.
To prevent further climate change-related damage, humanity must reduce its greenhouse gas emissions by moving away from fossil fuels and towards renewable energy sources like wind or solar power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These activities will help lower atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases and create a healthier environment for all life on Earth.
What are some possible solutions to climate change, and how effective are these solutions?
Climate change has become one of the most urgent issues of our time. It requires government, businesses and citizens to pay attention. A disrupted climate system is evident by rising temperatures, extreme weather events and increased sea levels. There are many solutions that can be used to combat this phenomenon. They range from technological solutions and behavioral changes to geoengineering.
Technological Solutions. There are many solutions to climate change that have been developed through technological changes. These include renewable energy sources like solar power and wind power that provide reliable sources for clean energy while causing minimal harm to the environment. By replacing petrol cars, electric cars that are powered by renewable energy can significantly reduce the amount of air pollution in cities. Reforestation projects are another technological option that aim to increase carbon sequestration, soil and trees. They also provide coastal protection systems to protect vulnerable areas from rising ocean levels.
Behavioral changes: Small adjustments to existing routines can make big differences in reducing emissions. This will help limit future climate disruption. For example, purchasing locally produced goods with shorter supply chains reduces emissions associated with transport costs for food. Also, using public or active transport instead of personal cars optimizes the use and reduces cost and air pollution. Additionally, home insulation that is more efficient can reduce dependence on gas boilers for heating your homes and lowers emissions.
Geo-engineering (GEO): This involves large-scale interventions into natural systems that may be too risky because of potentially unforeseeable consequences.
The effectiveness of these solutions largely depends on how much producers commit themselves towards investing in green alternatives; currently, initiatives such as using electric Cars tend expensive when compared with petrol versions however economic incentives favoring green investments play an integral role in incentivizing alternative solution uptake otherwise these remain mostly dormant when exposed only market forces which cannot guarantee their utility over time try apart from increasing consumer awareness over time regarding their efficiency hence mandating alternative solutions via policy measures represents one way forward however this needs regulatory bodies willing committed enough engaging players involved further still nontechnological approaches work one level but solving global warming phenomena requires all parties involved tackling issue earnest together.
How does human activity affect climate change
Climate change can be attributed to human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, humans have contributed more than 70% of global warming since mid-20th century.
Burning Fossil Fuels: Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This creates more atmospheric CO2, which acts like a "greenhouse" gas, trapping heat and increasing temperatures. As Arctic ice melts, this causes ocean levels to rise and can cause severe weather patterns all over the globe, including floods, droughts and storms that could lead to food shortages.
Deforestation - Trees which store atmospheric carbon dioxide within their trunks, when they absorb it through photosynthesis, are removed by deforestation. The albedo is also increased by cutting down forests. It refers to the amount of solar radiation reflected back into space. It also reduces the quality of local air, with deforestation being permanently linked to respiratory problems.
Farming: The animal agriculture industry contributes 14%-18% of total anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases globally every year. Animal waste releases large amounts of methane gas into the atmosphere due to its composition rich in methane bacteria Eating less or no animal products altogether can be an effective way to reduce your contribution towards global warming from this source alone., Agriculture itself also relies heavily on fertilizers which contain nitrous oxide released into our atmosphere directly harms humans creating smog from ground level ozone harming our respiratory system making polluted air hazardous for life.
Conclusion: Human activity has had a profound impact on the environment for centuries. However, technology has made it possible to leverage green innovation and make eco-friendly efforts to combat climate change. This will ensure that everyone is safe while prospering in nature.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to Incorporate Sustainable Practices Into Your Daily Life To Fight Climate Change
You can implement sustainable practices in your daily life by reducing your consumption. You can shop secondhand or borrow items from friends and family instead of purchasing new items every day. Additionally, eating vegetarian meals once or twice a week can help reduce the amount of methane released into the atmosphere from livestock production. For energy conservation, remember to turn off the lights whenever possible when leaving a space.
The other way to combat climate changes is to reduce carbon emissions from transportation such as cars and aircrafts. You can also choose renewable power sources like solar panels to replace traditional fossil fuels and generate electricity at your home. For climate action to be effective, it is essential that we support policy measures that promote clean air regulations. It is also a great idea to engage with others about issues like plastic pollution and forest destruction. This creates more informed citizens who will take action!