
Europeans are concerned about a range of issues, including climate change. These issues range from individual impacts to environmental destruction. There is a strong feeling that the world is warming and extreme weather events are increasing. Despite these difficulties, the European Union made commitments to decarbonize the planet and pledged to achieve its 2050 target. The region still faces challenges in a rapidly evolving global policy environment. Europe is also susceptible to the worst consequences of climate change.
Many countries in the region are expected to be affected by climate change. For example, Germany has a high proportion of people who are very concerned about the issue. Poland is the second-largest exporter of coal in Europe. However, the country has struggled with its coal production.
The EU biodiversity policy is an important part the European Green Deal. It aims to decarbonize and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. The strategy also calls on a 50% reduction in pesticides use by 2030. It also requires the restoration of 25,000 kilometers of rivers and Old-growth forests.
Young adults, particularly those between the ages of 18 and 29, are more concerned about climate change's personal impacts. This is especially true in Sweden. About 40% of young Swedes are concerned about climate change's potential effects.
Recent climate protests have been led by young people. Greta Thunberg from Sweden, a youth climate activist, is a strong force in Europe. Sweden is home to a greater proportion of adults concerned about climate change than any other country.
Young adults are also more concerned about climate change's impact on global ecosystems. They are also more likely be to adjust their lifestyles to deal with the problem. Similarly, the United States has a wide gap between older and younger people, with the oldest group more concerned about the harm of global climate change than the youngest.

Recent research showed that climate change concerns were increasing in the EU. Nearly all the countries that have trend data have experienced an increase in the number concerned citizens. Australia, Japan and Spain are just a few of the countries where there has been a double-digit increase in concern.
The worst affected by climate change in Europe will be Europe's most vulnerable populations. These countries are often the first to feel the effects of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and flooding. Moreover, the increased frequency of such events may increase the severity of diseases in humans and animals.
25% of the budget has been allocated by the European Union to combat climate change. A large portion of this budget will go to nature-based and biodiversity restoration. Moreover, the European Commission has launched a biodiversity strategy as a key part of the climate change mitigation strategy. The strategy calls for restoration of 25,000 km of rivers and a reduction of 50% in pesticide use.
FAQ
What impact does politics have on global efforts to tackle climate change?
Climate change is a highly politicized issue that has created a great deal of division among nations, governments, and individuals. The political stances taken by different actors will impact the implementation measures to combat climate changes. It is becoming difficult to reach consensus on global efforts for addressing this urgent environmental crisis.
The overwhelming majority of scientists agree with the fact that human-generated global warming is real. It is urgent for action to address it. These politics often hamper global cooperation needed to achieve effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices.
Many governments in the world want to protect their economic interests, and enforce measures that limit business activities. This often conflicts with the regulations that experts recommend to address climate change efficiently. Without strong commitments from all participating countries and wide-scale international action, it becomes very difficult for any single state or group of states to adequately address climate change through legislation or otherwise.
Further complicating the process of reaching full agreement on how to deal with climate change is the differences in power dynamics. Countries with more economic power often appoint their own representatives to represent them on international bodies responsible for negotiations over the environment - this can lead to lopsided discussions of those countries' perceived interests versus the collective interest of all involved parties. Additionally, the potential side effects of implementing radical changes like geoengineering are being heavily debated at both national as well international levels.
Also at the grassroots level, grassroots movements have fought against powerful opponents such as corporate ownerships. These lobbies are trying to preserve politically favorable positions for their industry especially when it is about funding research into alternative sources of energy production or enforcing Renewable Energy Technology mandates. If individual governments want to make valid progress in the subject matter themselves instead of seeking short-term benefits or spectacles, they must be clearheaded about possible outcomes.
Properly distributing resources allocated towards any intervention program while being mindful of political divisions between nations will be critical if any coordinated effort aimed at mitigating our current environmental crisis is going successfully to come to fruition.
What are the main causes of climate changes?
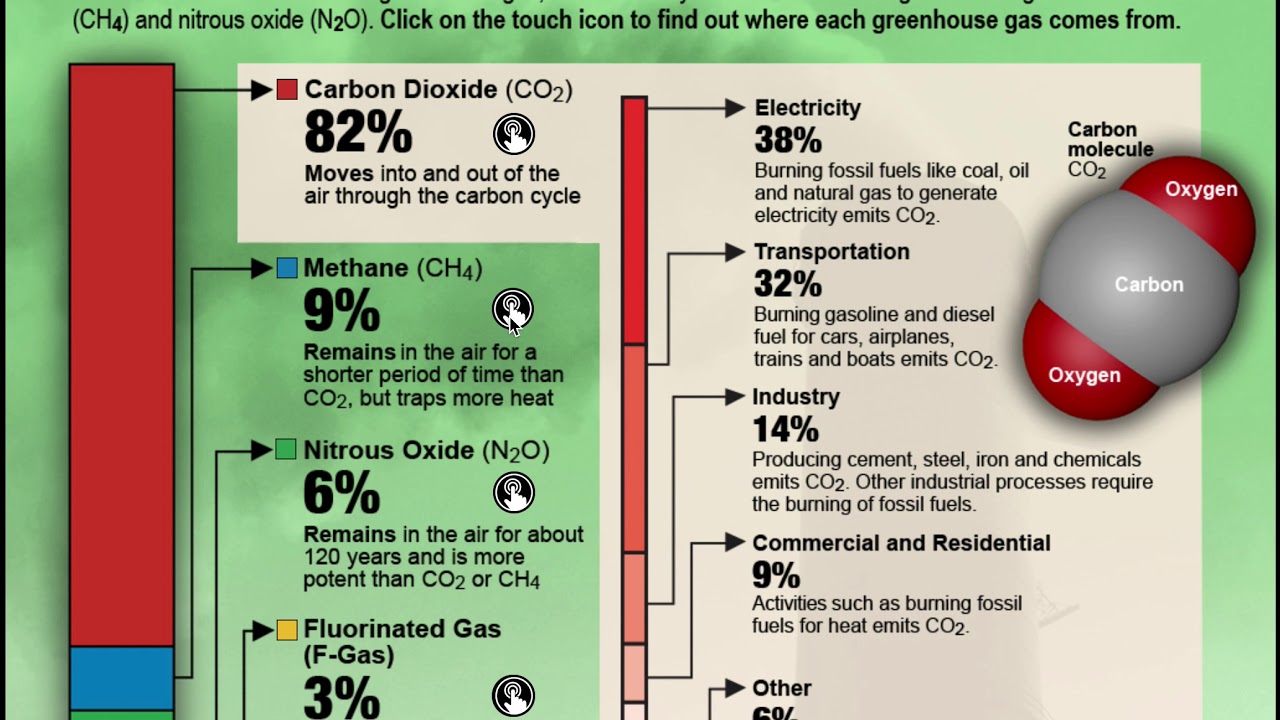
Climate change is a worldwide phenomenon caused by an increase of human-generated greenhouse gasses emitted into the atmosphere. This is mainly due to fossil fuel burning for power and transportation. These emissions cause more of the sun's warmth to be trapped in Earth's atmosphere, leading to rising global temperatures.
Other contributing factors to climate change are population growth, land clearance and destruction of ecosystems as well as deforestation, energy use, over-grazing and energy consumption. This reduces the amount of carbon sinks naturally found in the atmosphere that absorb CO2. Climate change can also come from natural forces, such as changes in solar energy.
These human activities together result in Earth experiencing an overloading of its energy budget. This has caused an average global rise of 1° Celsius over pre-industrial time. As the oceans absorb most heat energy, glaciers melt more quickly than they form. Other consequences include water shortages, droughts, and extreme weather events such as floods and hurricanes that are caused by heavy rainfall on saturated soils.
To prevent further damage, we must reduce our carbon footprint and cut our emissions as soon as possible. We can also take action now to mitigate the already severe effects of climate change. Along with reducing our dependence upon fossil fuels to generate electricity, it is important to invest in renewable sources like wind turbines or solar cells that do not emit harmful pollutants into nature. Also, reforestation is a sustainable practice that can restore balance to the delicate planetary cycles which are essential for our survival.
How will climate change impact the world's oceans?
What will climate change do to the oceans and marine life of the world?
Since its inception, climate change has had a significant impact on the oceans and marine life of the world. Constant oceanic heat from the depletion in the ozone layer causes major disruptions in marine ecosystems. This leads to coral bleaching, and decreases in species.
Climate change is also responsible for unpredictable weather patterns and stronger storms, which can lead to dangerously high sea levels. Additionally, temperature changes may cause water systems to lose oxygen. This can result in "dead areas" in which abundant marine life is reduced.
Ocean acidification is also a result of excess carbon dioxide that has built up in the oceans. This is due to climate change. Ocean acidification increases pH, which can disrupt the essential functions of animals that are unable to adapt, such as crabs, oysters, clams and crabs.
Higher temperatures can also change the location or shrinkage of natural habitats, making them less suitable for some species. Ocean stress increases already high extinction rates worldwide, creating a severe imbalance of predators and prey which might lead eventually to complete extinction.
The effects of climate change ripple throughout entire ecosystems influencing multiple species whether directly or indirectly through evaporation lowering water volumes or sharp temperature shifts jeopardizing any sustainable development for fisheries and other maritime activities. Global climate change continues to wipe out entire species of life on Earth, transforming our future lives not only on the land but also deep below the oceans' surface.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Support Climate-Friendly Policies and Companies
There are many ways that individuals can support climate-friendly companies and policies. This can include speaking out against non-climate-friendly businesses or politicians, voting for pro-environment candidates, writing letters or emails of encouragement to those who are already taking positive action towards the environment, and signing petitions in favor of policies that encourage and support climate-friendliness. Individuals can take practical steps like switching to greener providers or choosing more sustainable products than those that emit higher carbon emissions.
It is important to reduce one's carbon footprint in order to support climate-friendly companies and policies. This could be done by changing everyday habits such as not plugging appliances or turning off lights, using public transportation, carpooling or using other means to get around, and using eco-friendly household items such as biodegradable cleaning materials and composting kitchen leftovers.
Investors who are keen to support climate-friendly policies will want to find companies that produce lower carbon emissions before investing. Additionally, they should look into their portfolios periodically to ensure they meet the sustainability standards they have set themselves ahead of time. Investors may want to ensure that their investments in Green bonds do not finance projects with any activity which contributes more greenhouse gases into the air than they take away. Investors should look out for opportunities to use funds towards green business activities. This includes renewable energy alternatives, community-building projects, and initiatives that promote sustainability.