
Global temperature data illustrates fluctuations in both the global atmosphere and the oceans. These temperatures, and the impacts of them, can impact many natural processes, such as agriculture, and can cause illness and death in people. The increasing frequency of extreme heatwaves has led to millions of deaths and endangered ecosystems. Some regions are experiencing more warming than others.
Since the Industrial Revolution, global average temperatures have risen by approximately 2 degrees Fahrenheit. They also rose at an average of 0.18 degrees Celsius each decade since 1981. This is far beyond the long-term trend of warming. It's actually double the long term trend.
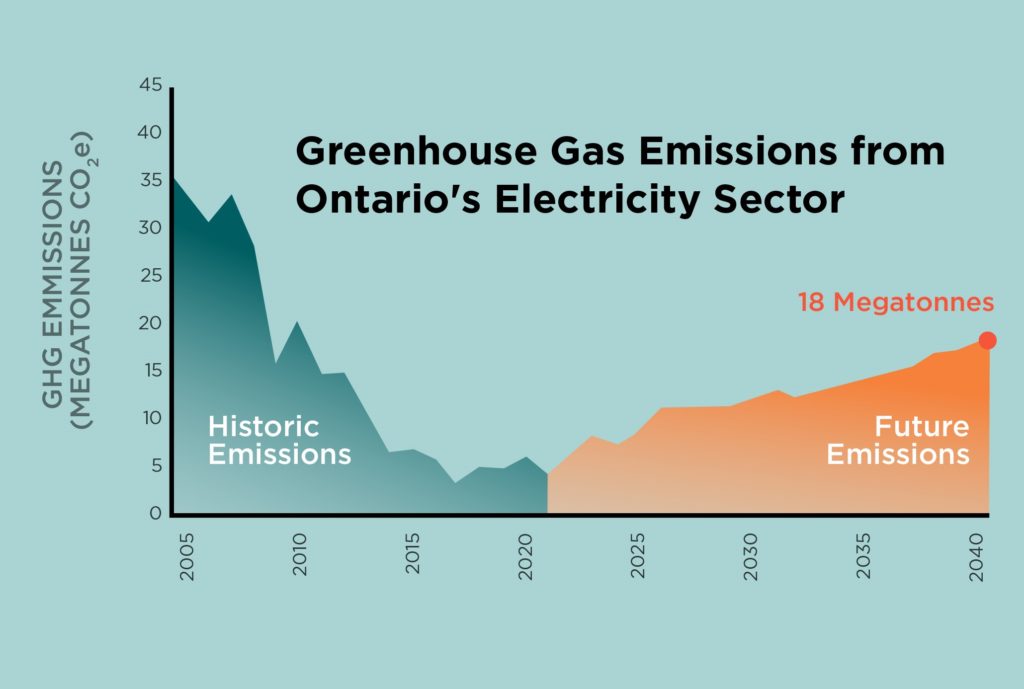
The current rate is higher than those of the 1980s, 1990s, and 1990s. This has had a huge impact on many areas from high-latitude to drier areas. It has also led to an increase in the intensity of tropical storms that are expected to have a significant impact on low-latitude areas.
As of January 2020 the global average surface temp is just 0.8 degree Celsius above the preindustrial level. Some subregions already have temperatures above 1.5 degrees Celsius. This level has not existed in the past ten years. Global warming has increased at a rapid pace over the past 30 years, exceeding 0.2 degrees Celsius per year for the last three decades. This rate will continue to rise in the future.
According to a recent WMO report, there's a 40% chance that global mean temperatures will surpass 1.5degC over the next five years. Some of these years, like 2021, are expected to be amongst the warmest ever recorded.
Although some regions experienced greater warming than others in 2015, the majority of the Earth's surface was warmer that normal during the first nine months. Most countries experienced temperatures above average. Some areas had record-breaking highs. Other regions, such as the southern United States and parts of South America, were among the warmest in recorded history.
Since the late 1970s, the United States has warmed at a faster rate than the global average. But, this trend is slowing in recent decades. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the global average temperature has increased by 0.17 degrees Celsius each decade. This is slightly more than the average temperature increase in the contiguous 48.
Climate change denier argue that global temperature is not an issue because the temperatures have remained fairly stable over the past few decades. Global surface temperature has increased much faster than it has declined, and scientists have found a direct correlation in climate change and extreme weather events.
According to the Goddard Institute for Space Studies, the average global land and ocean surface temperature was 1.2 degrees Celsius above the 1850-1900 average in 2010, and is expected to be 1.1 to 1.15 degrees Celsius above the pre-industrial average in 2022. If the rate of increase continues, that will put us on track to exceed 4 degC by the end of the century, which would result in unprecedented heat waves and severe drought in many regions.
FAQ
How can climate change impact food security and agriculture?
Climate change and global warming have a direct impact on agriculture and food security. The changing climate can affect rainfall patterns, temperatures, soil moisture levels, and extreme weather. This can disrupt farming activities, reduce crop yields and lead to losses of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures could lead to the growth of pests or diseases, which can have a negative impact on crops. This can lead to higher food costs and worsening nutrition.
Rising sea levels pose an additional threat, as they could inundate important agricultural land in many coastal regions, leading to increased salinity levels in wetlands where important crops are grown. The changing climate can also affect livestock production. High temperatures in summer months can decrease fertility rates in animals such as cattle, sheep, or goats. This can lead to lower milk yields that can increase food insecurity in communities.
Although the relationship between climate change, global warming, and other factors is complex, there are efforts being made by governments to mitigate them through adaptation strategies. These include strategic investments in climate smart agriculture (CSA), which allows governments around the globe to make strategic investments in adapting their agricultural systems. This includes promoting sustainable methods like crop rotation techniques and genetic diversity through conservation of native seed varieties. These help to protect against adverse impacts from extreme weather conditions and other environmental stressors due to the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
In order to ensure food safety in an ever-changing environment, farmers across the globe will need to use technologies that are more sensitive and adaptable to changing climates. There must be improvements made to existing infrastructure in order to take the appropriate actions when critical crop thresholds fall. This includes installing stable irrigation networks that provide adequate access water at times when it is difficult for farmers to grow crops. Collaboration between different stakeholders is needed to ensure that the quality nutrition guidelines are adhered to in all climates.
What role does climate change play in greenhouse gas emissions?
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act as an invisible layer around the Earth trapping infrared radiation. This warms the atmosphere. Without them, the planet would be much colder than it is today.
Greenhouse gases are generated through human activity, such as burning fossil fuels or other industries that produce emissions. As more heat enters the atmosphere from these activities, it leads to increased temperatures and extreme weather.
Carbon dioxide (CO2), the most potent greenhouse gas, is released by fossil fuels like gas, oil, and coal. Important contributors are also methane and nitrousoxide (N2O), as well fluorinated gases (Fgases).
The concentration of greenhouse gases has increased significantly since preindustrial times due to human activities. Global warming has resulted in an increase of temperatures around the world and in our oceans. It is also leading to changes such as intense storms and droughts; melting glaciers; and rising seas.
Humans must reduce greenhouse gas emissions to avoid further climate change damage. This can be done by switching from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These activities will lower the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gasses and make the Earth a more healthy place for all life.
What is the relationship between climate change and extreme weather events?
Extreme weather events, such as heat waves, floods, droughts, cyclones, storms, and hurricanes are directly linked to global warming. Global warming has contributed to an increase in the atmospheric temperature.
According to climate scientists, the frequency of extreme weather-related catastrophes has more than doubled in the past 20 years. The sea level rises due to rising ocean temperatures and changing wind patterns. This has an impact on the normal distribution and strength of hurricanes and storms across different regions of the planet.
2015 El Nino brought warm water towards South America. This led to increasing temperatures at an alarming pace and heavy rains that caused floods and displacement in Peru, Bolivia and other countries. Many places, including Antarctica has recorded its highest temperature ever. This is an indication of a strong correlation between global warming trends & the occurrence/frequency of extreme weather phenomena around the globe.
Another example is Hurricane Irma which took place in 2017 causing $50 billion of economic loss not just to the USA's Florida but also to other states such as Puerto Rico, Cuba, etc proving once again that climate change is responsible for a dramatic increase in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) concluded, "Human activities are increasing the severity current climate change." This naturally leads worldwide to more severe, intense, and frequent natural disasters. There is strong evidence of humans' involvement with extreme weather events occurring frequently around us all.
What is the current status of the global climate, and how is it changing in the future?
The current climate situation is one of uncertainty and unprecedented change. Unprecedented levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide are causing temperatures to increase significantly, leading to droughts, heat waves, changing rainfall patterns, melting polar ice caps, ocean acidification, and rising sea levels.
These changes already have a profound effect on ecosystems all over the globe, causing habitat destruction and extinctions. They also threaten the livelihoods and lives of billions, especially in areas that are already suffering from resource scarcity and poverty.
The number of extreme weather events - such as cyclones, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires - has been steadily growing over time due to higher average surface temperatures caused by human activity. This trend will continue as temperatures continue rising.
Global climate change can have a wide range of effects, including rising food security and displacement caused by extreme weather or sea-level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also contributing to existing social inequalities. Itdisproportionately affects marginalized communities, which lack the resources and knowledge required to adapt.
There has been progress in some areas, such as the reduction of carbon emissions or initiatives for renewable energy in certain countries. However, there is no global initiative that can be taken to effectively mitigate these changes. To prevent further destruction and devastation caused by climate change, all countries must work together to take immediate action and plan for adaptation in an ever-changing world.
What is climate change and how does it occur?
Climate change refers the long-term shifts that occur in global weather patterns due to an increase in greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to global temperature rises that can result in a range of climate and weather changes. This can include rising sea levels, melting glaciers, extreme storms and droughts, widespread coral reef bleaching, species extinction, and disruptions to food production.
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. These include burning fossil fuels, transporting electricity, cutting down trees, and farming livestock. When these activities release massive amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere it warms the planet at a much faster rate than natural processes like volcanic eruptions as these activities produce many times more emissions than volcanoes.
Deforestation also plays a large role contributing about 15-20% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Deforestation is when trees are cut down and burned. This releases carbon dioxide from the trees back into the atmosphere. Furthermore, forests act like a natural carbon sink and remove CO2 from air. Without this absorption capacity carbon dioxide levels will continue rising with devastating consequences to ecosystems all over the world.
In addition to releasing CO2 into the atmosphere, human-caused pollution also emits other harmful gasses such as methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O). Methane has been extensively used in industrial processes and contributes greatly to atmospheric warming. Meanwhile, N2O is emitted most commonly from agricultural soil management activities. For example, fertilization or tilling can release excess nitrogen into soil which results in N2O production upon contact with microbial organisms.
To minimize climate change humanity must make concerted efforts across social, economic, and political institutions to reduce these emissions drastically and transition away from our dependence on fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind power, or low-carbon hydrogen fuels. Replacing technologies that use polluting fossil fuels with smart solutions that promote zero-waste living could be an effective approach to decreasing atmospheric contamination while simultaneously reducing heating due to CO2 accumulation. It is possible to reduce our environmental footprint by taking responsibility. Conservation measures such as reforestation can help protect biodiversity and absorb large amounts of CO2 into the environment. This will be a powerful tool in helping to solve the climate crisis and restore balance for future generations.
Statistics
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Make Your Home More Energy-Efficient and Combat Climate Change
Energy efficiency can help you reduce your carbon footprint, cut down on your utility bills, make your life easier, and increase your comfort.
Make sure your home is well insulated and sealed. You should ensure windows and doors are correctly installed, check for drafts around pipes, vents, and add weather stripping where needed.
Insulate walls, ceilings and floors for maximum energy efficiency. You should inspect your attic and other areas for leaks.
Lighting is responsible for 18% of household electricity use. LED bulbs are up to 80% more efficient than traditional incandescent light bulbs. Installing motion sensors and timers will also help you save additional money by turning off lights as needed.
A newer model is more efficient and can help reduce your energy bills. Consider getting a programmable thermostat that allows you to set temperatures based on when people are home or away from the house.
You can replace all your windows with double-glazed windows that offer better insulation and heat resistance. Low-flow showerheads reduce water consumption and maintain adequate pressure.
Replace appliances with ENERGY STAR rated products since they use up to 50 % less power than non-certified models. You can save a lot of energy by not plugging in electronic devices such as TV boxes or phone chargers when they are not being used.
These steps can make living at home easier and less stressful.