
Scientists and other experts use scenarios to investigate the possible impacts of climate changes. They help communities and nations to make informed decisions about future adaptations or emissions. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change published a series containing a summary of peer-reviewed literature on possible scenarios. These reports synthesize the available evidence and provide a framework for interpreting and understanding climate change.
A typical scenario chooses a long term target and applies actions to that target. Some scenarios place caps and others set early or later climate policies. Scientists are able to create regional and national scenarios in addition to predicting the impact of future greenhouse gas emissions. The United States and Europe both have "Stated Policies Scenarios" which include policies regarding pricing, electrification, and efficiency.

There are two main types, baseline and mitigation. These are used to run climate models and compare the results. Similar to the baseline scenario the mitigation scenarios contain four forcing levels: 6, 4.5 and 3.4 W/m. Most of the scenarios also include a broader range of emissions options.
CMIP6, a global model of climate, is currently being developed. The modelling project also includes new scenarios for 1.9, 3.4 and 7.0. It also provides a range future emission scenarios, based upon the no-policy baseline. These scenarios, which are often based on the no-policy baseline, show how climate change may look in the future.
SRES A2 emission scenario, also known as business-as-usual scenario, is the first type. This scenario has a population that continues increasing while still producing carbon dioxide annually. It does not address the inequalities that exist between rich and poor nations. Although it may be politically diverse, the world in the SRES A2 emissions scenario remains fairly fossil fuel-dependent, with continued annual emissions.
SSP (Shared Socioeconomic Pathways) is another type of scenario. In these scenarios, global mean temperature increases range from 5.0 to 8.5 degC by 2100. It is not possible yet to run all SSPs through all models. However, there are computational limitations that limit the number and types of scenarios. These future scenarios are still the most popular.
One scenario that is frequently discussed in the scientific community is the RCP8.5, which is often referred to as the "business-as-usual" scenario. Researchers and scientists have criticized this scenario for its high emissions levels. The scenario could result in higher CO2 emissions than any other published one.
There is a lot of uncertainty in high-end scenarios regarding the projected energy intensity and carbon intensity. High-end scenarios also predicted rapid technological progress in carbon free technologies. They predicted that the prices of fossil fuels would increase and make these technologies competitive. This scenario did not include a large fossil fuel supply, which could explain the high emission levels.
NGFS or the Next Generation Framework for Scenarios is a collection a baseline and mitigation scenarios that reflect current trends in renewable power and other mitigation technologies. The project was completed by a team made up of economists, climate scientists, and economists. These scenarios have recently been updated with the most recent economic and climate data as well a number of policy commitments.
FAQ
What role can the energy sector play in climate changes?
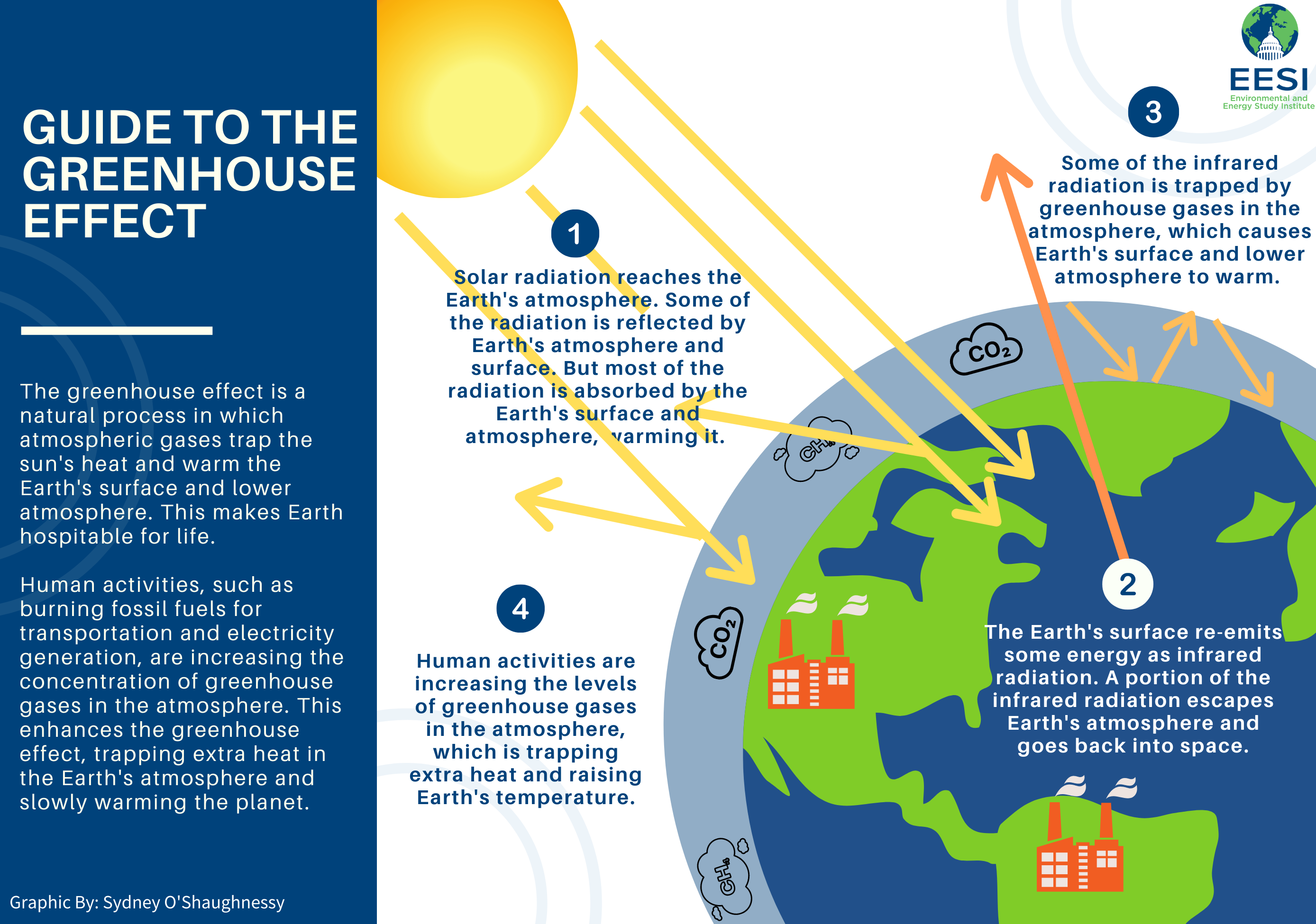
It is crucial that the energy sector plays a significant role in climate change. Global warming can be caused by the burning fossil fuels. The atmosphere releases carbon dioxide, trapping heat and leads to an increase in Earth's temperature.
To address this, energy sources must move away from carbon-emitting sources, such as coal and natural gas, and instead transition towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal. This change can be made by government policy, incentives, and investments in innovative technology, such as hydrogen fuel cells. Businesses and households will be able to reduce their carbon emissions and lower their electricity bills if they invest in infrastructure that supports renewable sources.
Other ways include switching from polluting transportation options such as petrol-fueled cars to moving towards electric or public transport. It is possible for governments to support battery technologies research and encourage people to use cleaner transportation.
Companies must also adopt green business practices to reduce their carbon footprint. This includes installing better insulation in offices and implementing energy efficiency plans at production plants. This will help reduce operational costs and improve environmental performance.
These initiatives must be championed not just at the company level but also at the government level for them to be truly effective; increasing taxes on pollution products encourages individuals to switch away from harmful practices without forcing them financially outcompeting polluters by providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products will create an ongoing market to support sustainability efforts moving forward. The private and public sector must work together to combat climate change. Providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products and switching to cleaner energy sources will create a market that supports sustainability efforts.
What impact does politics have on global efforts to tackle climate change?
Climate change is a highly politicized issue that has created a great deal of division among nations, governments, and individuals. Politicians of many actors influence the implementation of actions to address climate change. It has become difficult to find consensus on global efforts to tackle this pressing environmental crisis.
Scientific consensus is unanimous that human-caused climate change is real and needs to be addressed. These issues are often dominated by politics, which can hinder global cooperation that is necessary to implement sustainable energy practices, protect natural habitats, research viable technological solutions, as well as other climate change interventions.
In particular, various governments around the world are keen to protect their economic interests and enforce measures that would limit business activities as little as possible; this frequently conflicts with the regulations that experts recommend for addressing climate change in an efficient manner. Without strong commitments of all participating countries, and international action on a large scale, it becomes difficult for any state or group or states to effectively address climate-change legislation.
It is difficult to reach a consensus about how to address climate change because of differences in power dynamics between countries. Countries with more economic power frequently appoint their own representatives for international negotiations over the environment. This can lead lopsided discussions between countries' perceived interests and those of all other parties. The potential side effects of radical change like geoengineering, have been extensively discussed at both the national level and internationally.
The grassroots movements also have struggled against powerful enemies, such as corporate ownerships and well funded lobbyists who want to maintain politically favorable positions in their industries. This includes funding research into alternative forms energy production and enforcing renewable technology mandates. It is important that individual governments are clear about the possible rewards and outcomes if they intend to actively pursue valid progress on this matter and not seek public favor through short-term gains and spectacles.
To mitigate the current environmental crisis, it will be crucial that resources are properly distributed and political divisions between countries are not overlooked.
What does climate change mean for the oceans and marine life of the world?
What is the impact of climate change on the world's oceans and marine life?
Since its inception the climate change has had an impact on the world's oceans, and the marine life within them. Constant oceanic heat from the depletion in the ozone layer causes major disruptions in marine ecosystems. This leads to coral bleaching, and decreases in species.
Climate change may also be responsible for extreme sea level rises and more unpredictable weather conditions, which can prove to be fatal to coastal areas. Furthermore, changes in temperature may reduce oxygen levels in water systems resulting in "dead zones" where abundant marine life becomes sparse.
Ocean acidification is also a result of excess carbon dioxide that has built up in the oceans. This is due to climate change. Ocean acidification causes an increase in pH which affects the vital functions of animals such as crabs, clams, and oysters that cannot adapt to changing conditions.
Higher temperatures can alter the natural habitats of certain species by changing their locations or shrinking them, making them uninhabitable. An increase in ocean stress can accelerate already high extinction rates of many species around the world, resulting in a severe imbalance between predators/prey that could eventually lead to total extinction.
Climate change has ripple effects on entire ecosystems, affecting multiple species directly and indirectly. Evaporation, lowering water volumes, or temperature shifts can all impact sustainable development of fisheries and other maritime activities. The effects of climate change continue to impact the lives of entire species on this planet.
What is the current climate like? How is it changing?
The current state of the global climate is one of unprecedented change and uncertainty. Temperatures are increasing dramatically due to increased atmospheric carbon dioxide, which is leading to heat waves, droughts and changes in rainfall patterns.
These changes already have a profound impact upon ecosystems around the globe and are causing extinctions as well as disruption of habitats. They are also threatening millions of people's lives and livelihoods, particularly in areas where there is already resource scarcity.
Because of the increase in average surface temperatures from human activity, the number of extreme weather phenomena such as hurricanes and cyclones has been increasing steadily over time. This trend is expected to continue into the future as temperatures continue to climb.
Climate change has global consequences. It can affect everything, from food insecurity and displacement to communities that are forced to relocate due to severe weather events or rising sea levels. Climate change is also creating social inequalities bydisproportionately affecting marginalized populations that don't have the knowledge and resources necessary to adapt.
While there has been progressing in efforts such as reducing carbon emissions or renewable energy initiatives in some countries, we have yet to see meaningful action at a global level that would be necessary for mitigating these changes effectively. In order for us to prevent further disruption and devastation from climate change all nations must come together and take urgent action now while at the same time planning for adaptation in an increasingly uncertain world.
What are the roles of individuals and communities when it comes to addressing climate change?
Climate change is one the most pressing contemporary issues we are facing today. This issue affects everyone. It requires both our collective attention and individual action to make a positive difference.
Individuals have an essential role to play in addressing climate changes and reducing their effects. Your everyday behaviors could include reducing waste, conscious eating, changing your lifestyle, such as becoming vegetarian, choosing sustainable clothing and decor, and using public transport more frequently. They can also take part in advocacy and support initiatives that promote sustainability in their communities.
The key to addressing climate change at a larger scale is also the role of communities. They can implement policies that limit emissions by reformulating energy models based on renewable sources, promoting efficient infrastructure for cycling or electric transportation, reducing deforestation rates, or encouraging composting systems for waste management. For this mission to succeed, collaboration is key.
Moreover, civic education on the threats posed by climate change, as well as on ways to contribute positively towards tackling it needs to be implemented from the early stages of education acquisition throughout lifelong learning opportunities. This will make individuals more aware of the problems and help them understand the interconnectedness with societies farther away than their own.
Employers ultimately have a major role in fighting climate change. Implementing corporate practices that focus on sustainability and opting to use green alternatives whenever possible will yield both sociologically and economically positive results.
Individual and community actions combined with policies at the local level, as well as business transformation, will make a huge contribution to addressing global warming. They also help to protect humanity from long term harmful effects resulting from climate change.
What is the impact of climate change on biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change has many effects on biodiversity and ecosystems. The most pressing issues facing wildlife and ecosystems are rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and increased acidity.
These shifts in climate conditions can cause shifts in habitat areas, disrupt food chains or affect population numbers or species distributions, with potentially dramatic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems. The hydrological cycle changes can have an impact on the availability of water for aquatic species.
Moreover, changes to climate result in rising temperatures and more frequent extremes such as droughts and floods which puts more stress on already fragile systems such as coral reefs or tropical rainforests. A climate change scenario could see up to 30% loss of animal species by 2050. That would trigger a chain reaction of losses within eco-systems.
Climate change is an enormous threat to biodiversity and to human societies which depend on functioning ecosystems. The best way to minimize its impact is to work at every level to reduce global warming trends. Future damages can be avoided with prudent management practices.
How does climate change and global heating impact agriculture and food safety?
Climate change and global warming are directly impacting agriculture and food security. Changes in climate can have an impact on rainfall patterns, temperature, soil moisture, extreme weather, and other aspects of agriculture. This can lead to disruptions in farming activities, lower crop yields, and loss of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures could lead to the growth of pests or diseases, which can have a negative impact on crops. This can lead to higher food costs and worsening nutrition.
Rising sea levels pose an additional threat, as they could inundate important agricultural land in many coastal regions, leading to increased salinity levels in wetlands where important crops are grown. Climate change can also impact livestock production. Warm summer temperatures can reduce the fertility of animals like cows, sheep, and goats. This can cause lower milk yields and increase food insecurity within communities.
Global warming and climate change have a complicated relationship. However, adaptation strategies are being implemented by governments globally through strategic investments made in climate-smart farming (CSA). This involves encouraging sustainable methods, such a crop rotation technique or the conservation of indigenous seed varieties. This helps to mitigate adverse effects from changing weather or other environmental stressors. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. Existing infrastructure must be improved to allow for the appropriate action when necessary. This includes stabilizing irrigation networks that have adequate access to water during periods when there are less water sources due either to extreme downpours or warmer climates. For sustainable solutions to be created that will ensure the continued compliance with international dietary guidelines in our ever-changing climates, it is necessary to have a cohesive collaboration among all stakeholders. This includes government officials at international levels as well as NGOs located at local communities.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Support Climate-Friendly Businesses and Policies
There are many ways that individuals can support climate-friendly companies and policies. This can include speaking out against non-climate-friendly businesses or politicians, voting for pro-environment candidates, writing letters or emails of encouragement to those who are already taking positive action towards the environment, and signing petitions in favor of policies that encourage and support climate-friendliness. Individuals may also be able to take more concrete steps, such as switching to eco-friendly providers and choosing sustainable products over higher carbon emissions.
In order to support climate-friendly policies, it is crucial that one reduces his or her carbon footprint. This could be done by changing everyday habits such as not plugging appliances or turning off lights, using public transportation, carpooling or using other means to get around, and using eco-friendly household items such as biodegradable cleaning materials and composting kitchen leftovers.
Investors who are keen to support climate-friendly policies will want to find companies that produce lower carbon emissions before investing. Additionally, they should look into their portfolios periodically to ensure they meet the sustainability standards they have set themselves ahead of time. Green bond investors may be concerned that they do not invest in activities that emit more greenhouse gases than they take out. Lastly, investors should pay attention to any opportunities where funds could be transitioned towards green business activities such as renewable energy alternatives as well as other initiatives promoting sustainability such as community-building projects focused on green technologies.