When it comes to climate change, the European public is concerned about a variety of issues. They can be personal or environmental. There is a growing sense that the planet is warming rapidly and that extreme weather is becoming more common. Despite these difficulties, the European Union made commitments to decarbonize the planet and pledged to achieve its 2050 target. The region still faces many challenges in an ever-changing global policy environment. Europe is particularly vulnerable to the worst effects climate change has on it.
Many countries in the region are expected to be affected by climate change. Germany is one example of a country that has high levels of concern about climate change. The country also produces the second largest amount of coal in EU, behind Poland. Despite its large coal production, the country has struggled to decrease it.

The EU biodiversity policy is an important part the European Green Deal. It aims to decarbonize and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, the strategy calls to a 50% reduction of pesticides in 2030. It also calls for the restoration and maintenance of 25,000 kilometers old-growth forests.
Young adults, especially those between 18 and 29, are more concerned with the personal effects of climate change than older adults. This is especially true of Sweden. About 40% of young Swedes are concerned about climate change's potential effects.
Recent protests against climate change have been led by young people. Greta Thunberg, a Swedish youth climate activist, is an example of a prominent European force. Sweden has a higher number of adults than other countries who are concerned about the climate change-related harm.
Young adults are also more likely than older adults to be concerned about the impact of climate change upon global ecosystems. They are also more likely be to adjust their lifestyles to deal with the problem. The United States has a wide disparity between older and younger citizens, with the older group being more concerned by the impact of global warming than the younger.

Recent studies have shown that EU citizens are more concerned about climate change. Nearly all countries with trend data have seen an increase in very concerned citizens. Some countries with double-digit increases in concern include Australia, Spain, Japan, and the United Kingdom.
Climate change will affect Europe's poorest people the most. These countries are most often first to be hit by extreme weather events such as droughts, floods and heatwaves. These events can also increase the severity and frequency of disease in animals and humans.
25% of the budget of the European Union has been dedicated to fighting climate change. This budget will be used for nature-based solutions as well as restoring biodiversity. Moreover, the European Commission has launched a biodiversity strategy as a key part of the climate change mitigation strategy. The strategy calls for the restoration and reduction of pesticides by 50%.
FAQ
What is the current status of the global climate, and how is it changing in the future?
The current climate situation is one of uncertainty and unprecedented change. Unprecedented atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide are leading to significant temperature increases, including droughts, heat waves and changing rainfall patterns. They also cause ocean acidification, rising sea levels, and melting polarice caps.
These changes have already had a significant impact on ecosystems across the globe, leading to habitat loss and extinction. They are also threatening lives and livelihoods for billions of people, especially those who live in areas with resource scarcity.
The number of extreme weather events - such as cyclones, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires - has been steadily growing over time due to higher average surface temperatures caused by human activity. As temperatures rise, this trend will likely continue.
The effects of a rapidly changing global climate can be felt everywhere from rising food insecurity to displacement from extreme weather events or sea level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also exacerbating existing social inequalities by disproportionately affecting marginalized communities that do not possess the resources or knowledge necessary for adapting effectively.
While some countries have made progress in reducing carbon emissions, or implementing renewable energy initiatives, global action has not been taken at the level necessary to combat these changes. All nations must unite to prevent further destruction and devastation by climate change.
How does climate change impact marine life and oceans around the globe?
What are the effects of climate change on oceans and marine life around the globe?
Since its inception climate change has significantly affected the world's oceans as well as the marine life associated with them. Constant oceanic warming due to the depleted ozone layer causes drastic disruptions in marine ecosystems resulting in a decrease in species and coral bleaching.
Unpredictable weather conditions and stronger storms are also linked to climate change, leading to extreme surges in sea levels that can prove deadly for coastal areas. Additionally, temperature changes may cause water systems to lose oxygen. This can result in "dead areas" in which abundant marine life is reduced.
Ocean acidification is also a result of excess carbon dioxide that has built up in the oceans. This is due to climate change. Ocean acidification can raise pH levels, making it difficult for animals to adapt like crabs, clams or oysters.
Higher temperatures can also cause changes in natural habitats. They may shrink or change their geographical location, making it unhabitable for species that depend on them. The increase in ocean stresses accelerates the already high rates of extinction worldwide. This can lead to a severe imbalance among predators and prey, which could ultimately lead to complete extinction.
All ecosystems are affected by climate change. This can be directly or indirectly via evaporation, water volume reductions or sharp temperature shifts. These changes could have a devastating effect on sustainable development of marine activities and fisheries. The effects of climate change continue to impact the lives of entire species on this planet.
What role can the energy sector play in climate changes?
It is crucial that the energy sector plays a significant role in climate change. Global warming is caused by the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This traps heat and causes an increase in Earth's average temperature.
To address this, energy sources must move away from carbon-emitting sources, such as coal and natural gas, and instead transition towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal. This transition can be made through both government policy and incentives, as well as investments in innovative technology like hydrogen fuel cell. Businesses and households can both reduce their carbon footprints while also lowering their electricity bills by investing into infrastructure that supports this use of renewable resources.
Other ways include switching from polluting transportation options such as petrol-fueled cars to moving towards electric or public transport. Governments can help lead society's transition from oil-based infrastructures to cleaner alternatives by funding research into battery technologies and encouraging consumers to make investments in cleaner modes.
Companies must also adopt green business practices to reduce their carbon footprint. This includes installing better insulation in offices and implementing energy efficiency plans at production plants. This will help reduce operational costs and improve environmental performance.
These initiatives should be championed at all levels, not just at company level but also at government. Raising taxes on pollution products encourages individuals and businesses to stop using harmful practices. While this may be a financial outlay for polluters, providing vouchers for or subsidy for low-carbon products can create a continuing market to support sustainability efforts. It is important to recognize that tackling climate change takes a lot of effort from both the private and public sectors.
What is the role of greenhouse gases in climate change?
Greenhouse gases play a major role in climate change. They act as an invisible layer around the Earth trapping infrared radiation. This warms the atmosphere. Without them, the planet might be much colder that it is now.
Greenhouse gases are generated through human activity, such as burning fossil fuels or other industries that produce emissions. As these activities continue to increase, more heat gets trapped in the atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
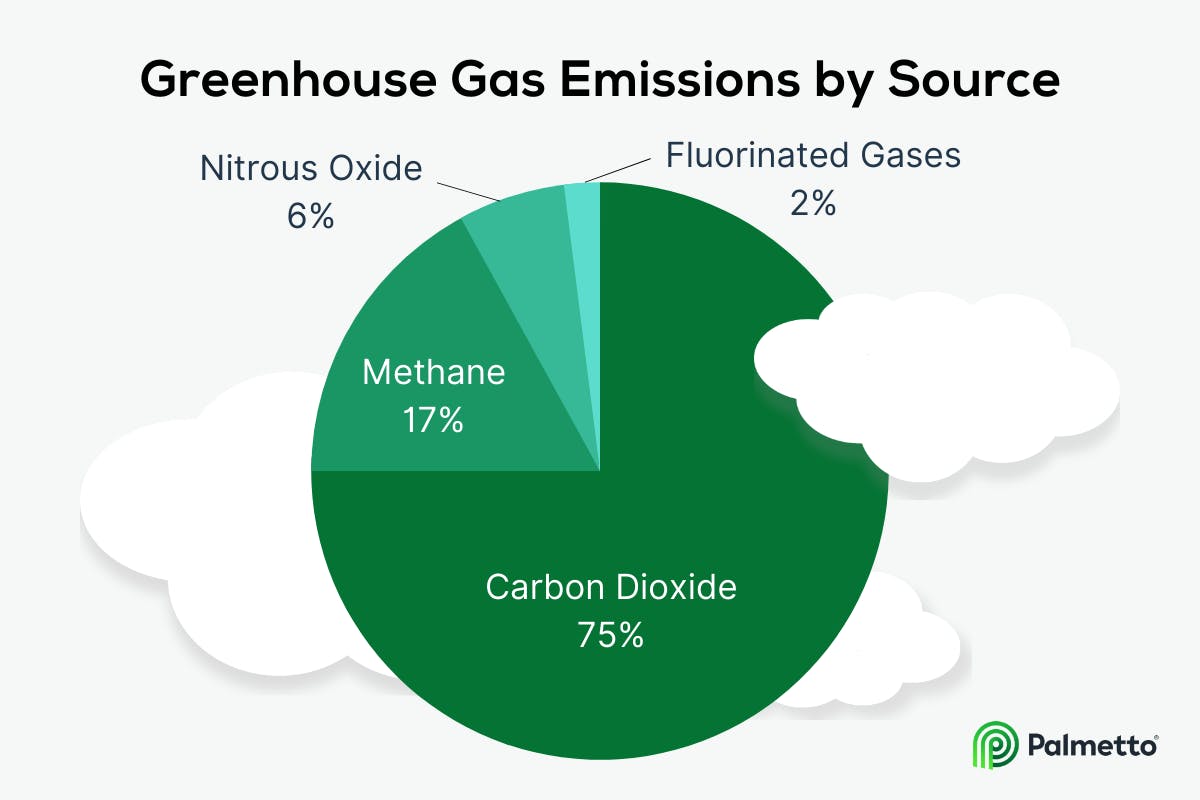
The most abundant greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide (CO2), which is released when burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas. Important contributors are also methane and nitrousoxide (N2O), as well fluorinated gases (Fgases).
The concentration of greenhouse gases has increased significantly since preindustrial times due to human activities. This has led both to global warming and an increase worldwide in temperatures, as well as increased ocean levels. It is also causing changes such as more intense storms and droughts, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels.
To avoid further damage from climate change, humans need to reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases by transitioning away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. You can also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reforestation and adopting farming methods that allow soil to absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These activities will lower the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gasses and make the Earth a more healthy place for all life.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest Clean Energy and Support a Transition to a Low Carbon Future
Clean energy is a type of renewable power that doesn't produce any pollution or emit carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases. It includes technologies such as solar photovoltaic, wind power, hydroelectricity, geothermal energy, and hydrogen fuel cells. Clean energy sources offer many environmental benefits. These include a reduction in dependence on fossil fuels, reduced air pollution from traditional electricity methods, and more reliable access to remote areas.
Investors have the opportunity to invest in clean-energy projects by purchasing shares of companies that create innovative technologies. This includes investing directly in stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) related to clean energy. Direct investments in start-ups and venture capital projects can be an option for investors to help fund research and development of clean energy technologies.
Clean energy investors support innovation that reduces harmful emissions from electricity generation. This investment could lead to greater economic development as it may create jobs in the field of producing renewable energy systems, which require engineers and skilled labor. Finally, putting money into clean energy can provide investors with a financial return due to tax incentives programs that are incentivizing investments into green technologies like wind farms, solar panels, and biomass heat generation systems.
We can help the transition to low-carbon by investing in companies that create electricity from renewable resources.